
|
|
|
|
|

|
Marinefliegergeschwader 5 “Kiel”; Kiel-Holtenau, June 24, 2000
The Helicopters of the German Navy; Text and Photograph's by Alex van Noye
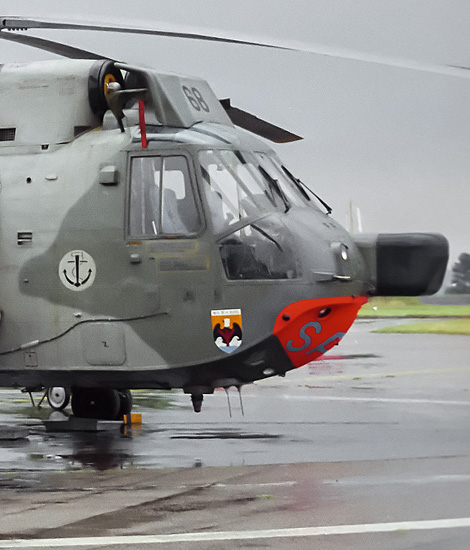
Nowadays Marinefliegergeschwader 5 (MFG-5) is stationed at the North German Naval Base Kiel-Holtenau. The unit houses two operational helicopter types which are equipped with the Sea Lynx Mk88 and the Sea-King Mk41. The unit has the Search And Rescue task along the German coastline and aboard the ships.
The airport of Kiel-Holtenau is located at the end of the Kiel Canal on the Kiel Fjord near the Baltic Sea and is known for its large locks for ocean-going vessels and the location of Kiel Airport. To the north of the city of Kiel-Holtenau lies the Olympic port in Kiel-Schilksee. The helicopters are stationed on a relatively small compound at the southern part of the airfield. In the weapon of MFG-5 are the elements water, a sea eagle, an anchor and a swivel arm visible. The sea eagle watches over the troubled sea. The swivel arm and the anchor symbolize that the unit is part of the German Navy Service. The coat of arms of Marinefliegergeschwader 5 was designed by boatswain Fritz Safert. In the original weapon the eagle had a black head and the bird looked to the right. The feathered wings were smooth. There was one blue and one white wing visible. It symbolized all the life that was saved from death and danger by the eagle. This weapon was already used in the lifeboats during the Second World War. In 1962, the waves were improved and replaced by two white waves and four round blue waves. The line of sight of the eagle has also changed. On the occasion of the 1972 Olympics in Kiel, the eagle got a more dynamic expression through the now turned in wings. Before the open house of 1975, the coat of arms received its last form at the time when MFG 5 was established in Kiel. The black eagle changed into a bald eagle with a feathered white head that was suitable for the area of operations.
Kiel Airport was built in 1914 on an area that had been leveled with the excavation of the Kiel Canal. In 1927, the Kiel Airport Company (Kiel FlugGrup, KFG) was established, which in the following years operated the airport of Kiel. 27 national and international destinations were served. In 1937, the airport was transformed into a military airfield. During the Second World War, several German Navy units were stationed at Kiel. Shortly before the war there were still units of the German Luftwaffe on this field. However, during the Second World War, more and more navy units were
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
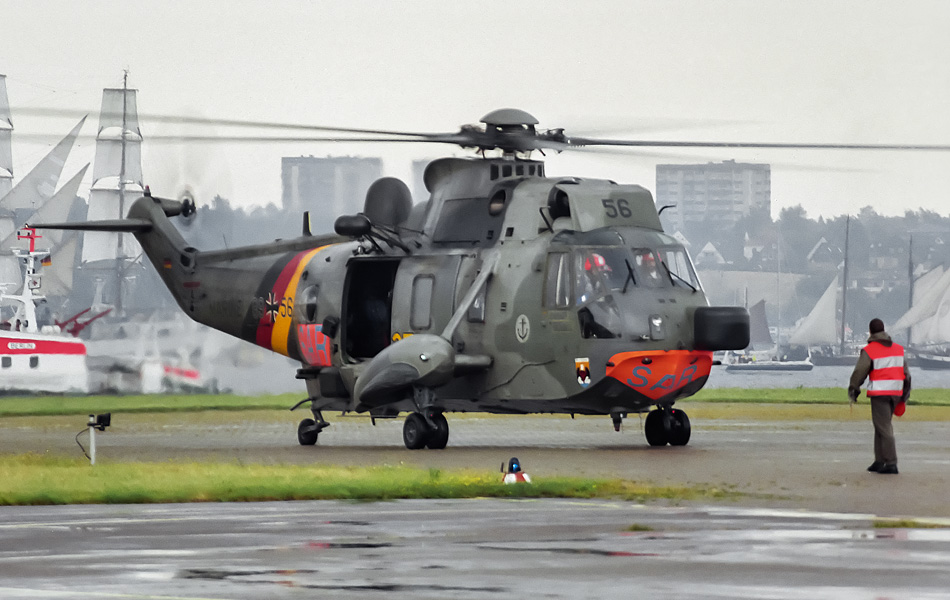
placed at this airport. The German Navy was at that time planning to build an aircraft carrier. The flying units would be based on land at Kiel. However, these plans did not go through in the course of the war. After the Second World War, nothing happened for a long time on the military part of Kiel. In 1963, an extension of taxiways took place and in 1965 the first terminal building was built on the civil part of the airfield. On January 1, 1958, frigate captain Heinz Seebens was commissioned to set up a naval air navigation service for rescue operations at sea. This unit was established as MFG-5 on January 4, 1958. The unit was equipped with Sikorsky S-58 helicopters for SAR duties. In the early seventies, the Albatross and the Pembroke which flew in the transport role were replaced by the Dornier Do-28. In 1975, the last Sikorsky H-34 helicopters were replaced by the current Sea-King Mk41 and later the Sea-Lynx Mk88 was added at the beginning of the 80s.
The only unit of the German Navy which currently is operating with helicopters is Marinefliegergeschwader 5 (MFG-5). This unit is stationed at the North German airbase Kiel-Holtenau. MFG-5 also has the name Kiel in his designation to honor the famous naval port. All rotary wing equipment is accommodated at MFG-5. The German Navy currently has two types of helicopters in use; the Westland Sea-Lynx Mk88 and the Westland Sea-King Mk41. The Sea-King is the largest helicopter in use by the German Navy. The helicopters have been delivered to the German Navy since 1973. In total, the navy received 22 helicopters of the type Sea-King Mk41. The aircraft replaced the Grumman Albatross flying boat in the SAR role. The German Navy was the first export customer to buy the Westland Sea-King in SAR configuration. The helicopters were stationed at Kiel and were equipped with radar and modern navigation equipment. An extra helicopter was purchased to replace a crashed Sea-King in 1975. The Sea-King is able to transport the Sea Skua anti-ship missile. To use this rocket, the Ferranti Seaspray radar was built into the nose of the helicopter. The helicopters are mainly deployed in Germany in the SAR role along the North Sea coastline and the Baltic coastline. Kiel is centrally located along the German coastline, allowing the helicopters to monitor the entire coastline from this base. The Sea-King is often stationed on frigates and can also be used for military operations. The helicopter is suitable to transport 18 men in this role.
The Sea Lynx Mk88 was first used in Germany in 1981. A total of 19 helicopters of this type have been built. The Lynx Mk88 is a variant specially developed for the German Navy. In 1996, the German Navy ordered another seven Super Lynx Mk88A helicopters. In 1998, the Lynx fleet was fully updated to the Lynx Mk88A standard. The Lynx was given the opportunity to carry the Sea Skua anti-ship rocket. Later, the Lynx underwent another update. The Super Lynx was brought to the same standard as the Sea Lynx. The German government signed a contract to provide the helicopters with a Selex ES system that contained Electro optical and infrared sensors. The helicopters of the navy can be equipped with Torpedoes and light rockets. Also, machine guns can be mounted in the doors on the sides of the helicopters. This armament plays an important role during tactical flights such as anti-piracy missions. The primary tasks of the Lynx are exploration above sea and target data analyzes. The Lynx is also used for attacking of targets at the water surface. The helicopter is often also used to track submarines and for SAR tasks above the sea in the event of missions and evacuations. Transporting materials and personnel above the sea is a task that is also regularly carried out by the Lynx. At the moment the German navy is using 22 helicopters of the type Sea Lynx. The Sea Lynx is a helicopter that sails with the German Navy on the frigates.
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|
|

|







